- 메일 주소 : David@tmaxcn.com
- 메일 주소 : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
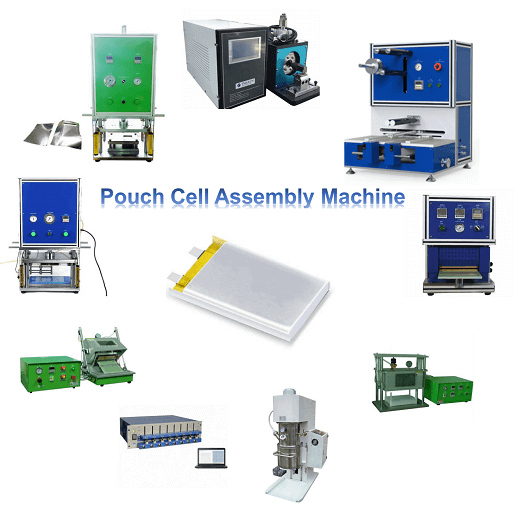
The production line of pouch cell, a type of lithium-ion battery known for its flexibility and lightweight design, involves several key stages. Each stage utilizes specialized equipment to ensure the precise assembly and performance of the batteries. Below is an overview of the equipment and their roles in the pouch cell assembly line:
1. Coating Equipment:
Role: Applied in the electrode manufacturing stage, coating equipment is used to apply a thin layer of electrode slurry onto the current collector, typically made of aluminum for the cathode and copper for the anode. This slurry contains active materials, conductive additives, and a binder.
2. Drying Ovens:
Role: After coating, the electrode sheets are passed through drying ovens to remove solvents from the slurry. This step is crucial for ensuring the stability and integrity of the electrodes.
3. Electrode Cutting Machine:
Role: Once the electrodes are dried, they are cut into specific sizes and shapes using electrode cutting machines. Precision in cutting is essential to meet the design specifications of the pouch cell.
4. Separator Coating Equipment:
Role: A separator is coated with a thin layer of ceramic or polymer material to enhance its properties. This coating prevents the electrodes from coming into direct contact, avoiding short circuits.
5. Pouch Cell Formation Equipment:
Role: Pouch cell formation equipment assembles the battery by stacking the coated electrodes, separators, and electrolyte-soaked separator layers. This forms the basic structure of the pouch cell.
6. Tab Welding Machine:
Role: Tabs are welded onto the electrodes to create electrical connections. Tab welding machines use precision welding techniques to ensure a reliable connection.
7. Electrolyte Filling Equipment:
Role: Electrolyte filling equipment injects a precise amount of electrolyte into the pouch cell. This step is critical for the electrochemical reactions within the battery.
8. Sealing Equipment:
Role: The pouch cell is sealed to prevent leakage and ensure a hermetic seal. Sealing equipment often uses heat or ultrasonic welding to securely seal the edges of the pouch.
9. Formation and Aging Chambers:
Role: Pouch cells undergo a formation process in specialized chambers where they are charged and discharged multiple times to stabilize their performance. Aging chambers simulate real-world usage conditions, ensuring the reliability of the batteries.
10. Voltage Testing Equipment:
Role: After formation and aging, each pouch cell undergoes voltage testing to verify its electrical characteristics. Cells that do not meet specified voltage parameters are rejected.
11. Laser Welding Machine:
Role: Laser welding machines are used to connect the external leads to the tabs of the pouch cell. This process ensures a secure and efficient electrical connection.
12. Quality Control Systems:
Role: Throughout the pouch cell production plant, quality control systems monitor various parameters, including dimensions, electrical characteristics, and visual defects, to ensure that each pouch cell meets the required quality standards.
13. Formation Testing Equipment:
Role: Pouch cells undergo additional formation testing to verify their capacity, voltage, and overall performance under load conditions.
14. Packaging Equipment:
Role: The final stage involves packaging the pouch cells, often in multi-cell configurations, for distribution and use in various applications, such as electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and energy storage systems.
The pouch cell production line is a complex and highly controlled process that integrates these specialized equipment and stages to produce high-performance lithium-ion batteries for diverse applications.
 English▼
English▼




 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

