- 메일 주소 : David@tmaxcn.com
- 메일 주소 : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
블로그
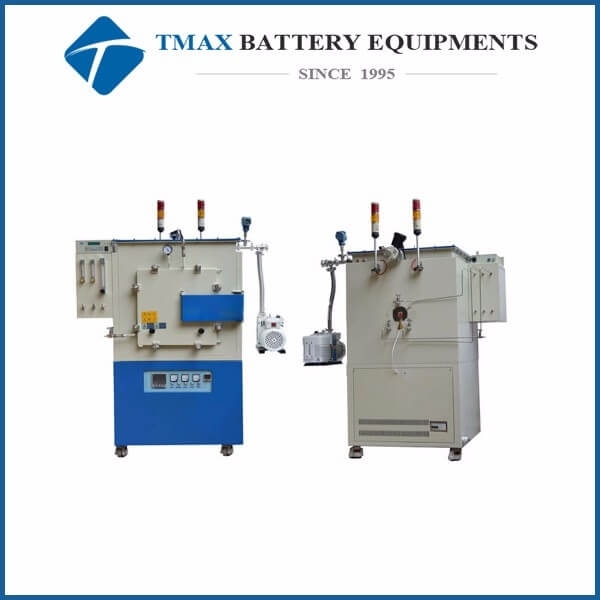
Hydrogen Furnace
A hydrogen furnace is a specialized type of furnace used in material processing, heat treatment, and synthesis applications. It operates in an atmosphere enriched with hydrogen gas, which serves as both a protective and reactive environment. This makes hydrogen furnaces ideal for processes requiring high purity, reduction of oxides, or the prevention of oxidation during heating.
In this article, we will explore the design, operation, advantages, challenges, and applications of hydrogen furnaces.
●Design and Operation of Hydrogen Furnaces
1. Key Components
Chamber: The main enclosure where the material is heated under a controlled hydrogen atmosphere.
Heating Elements: Typically made of materials resistant to high temperatures and hydrogen exposure, such as silicon carbide or molybdenum.
Hydrogen Supply System: Ensures a continuous flow of pure hydrogen into the chamber.
Exhaust System: Safely removes excess hydrogen and byproducts from the chamber.
Temperature Control System: Monitors and regulates the temperature within the furnace.
2. Operation Principle
The material to be processed is placed inside the furnace chamber.
Hydrogen gas is introduced into the chamber, creating a reducing or inert atmosphere.
The heating elements raise the temperature to the desired level, allowing the material to undergo the intended process (e.g., sintering, annealing, or oxide reduction).
After processing, the material is cooled under a controlled hydrogen atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
●Functionalities of Hydrogen Furnaces
1. Oxide Reduction:
Hydrogen acts as a reducing agent, converting metal oxides back to their metallic forms.
2. Protection Against Oxidation:
Prevents the formation of oxides on metals during hightemperature processes.
3. Sintering:
Used for sintering powdered metals or ceramics to achieve highdensity components.
4. Annealing:
Improves the mechanical properties of metals by relieving internal stresses and refining grain structure.
5. Material Synthesis:
Facilitates the synthesis of advanced materials, such as metal hydrides or nanostructured compounds.
●Advantages of Hydrogen Furnaces
1. High Purity Environment:
Hydrogen provides a clean atmosphere, minimizing contamination during processing.
2. Efficient Reduction:
Effectively reduces metal oxides, enabling the production of highpurity materials.
3. Versatility:
Suitable for a wide range of processes, including sintering, annealing, and brazing.
4. Uniform Heating:
Advanced temperature control systems ensure consistent heating across the entire chamber.
5. Scalability:
Available in laboratoryscale and industrialscale models to meet diverse needs.
●Challenges in Using Hydrogen Furnaces
1. Safety Concerns:
Hydrogen is highly flammable and requires strict safety measures to prevent leaks or explosions.
2. Cost:
Highquality hydrogen furnaces and pure hydrogen gas can be expensive.
3. Material Compatibility:
Some materials may react with hydrogen at high temperatures, leading to undesirable effects.
4. Maintenance:
Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure the integrity of seals and heating elements.
5. Complexity:
Requires precise control of hydrogen flow rates and pressure to achieve optimal results.
●Innovations in Hydrogen Furnaces
To address these challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are incorporating advanced technologies:
1. Improved Safety Systems:
Integrated sensors and alarms to detect hydrogen leaks and maintain safe operating conditions.
2. Energy Efficiency:
Advanced insulation and heat recovery systems to reduce energy consumption.
3. Automation:
Programmable controls for precise parameter adjustments and unattended operation.
4. Advanced Materials:
Use of corrosionresistant materials for furnace components exposed to hydrogen.
5. Smart Monitoring:
Realtime data analytics tools for continuous monitoring of processing conditions.
●Applications of Hydrogen Furnaces
Hydrogen furnaces are used across various industries and research fields:
1. Metallurgy:
Sintering of powdered metals to produce highdensity components.
Annealing of steel and other alloys to improve ductility and strength.
2. Ceramics:
Reduction of ceramic oxides for the production of advanced materials.
3. Electronics:
Fabrication of semiconductor materials and thin films under controlled atmospheres.
4. Automotive Industry:
Brazing and heat treatment of automotive parts to enhance durability.
5. Research and Development:
Synthesis of new materials, such as metal hydrides and nanostructures.
●The Future of Hydrogen Furnaces
As technology advances, hydrogen furnaces will continue to evolve to meet the demands of emerging applications. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous systems will optimize processing parameters and reduce human intervention.
2. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and energyefficient designs will become integral parts of future systems.
3. Integration with Advanced Technologies:
IoTenabled furnaces will connect to smart labs for realtime data analysis and process optimization.
4. Development of New Materials:
Advances in hydrogencompatible materials will enable processing of even more challenging substances.
5. Hydrogen Economy:
As hydrogen becomes a key player in the global energy transition, hydrogen furnaces will play a crucial role in material processing and synthesis.
●Conclusion
Hydrogen furnaces are indispensable tools for material processing, offering a unique combination of high purity, efficient reduction, and versatility. Their ability to operate in a controlled hydrogen atmosphere makes them essential for producing advanced materials and improving the properties of metals and ceramics.
November 28,2025.
Xiamen Tmax Battery Equipments Limited was set up as a manufacturer in 1995, dealing with lithium battery equipments, technology, etc. We have total manufacturing facilities of around 200000 square foot and more than 230 staff. Owning a group of experie-nced engineers and staffs, we can bring you not only reliable products and technology, but also excellent services and real value you will expect and enjoy.
A hydrogen furnace is a specialized type of furnace used in material processing, heat treatment, and synthesis applications. It operates in an atmosphere enriched with hydrogen gas, which serves as both a protective and reactive environment. This makes hydrogen furnaces ideal for processes requiring high purity, reduction of oxides, or the prevention of oxidation during heating.
In this article, we will explore the design, operation, advantages, challenges, and applications of hydrogen furnaces.
●Design and Operation of Hydrogen Furnaces
1. Key Components
Chamber: The main enclosure where the material is heated under a controlled hydrogen atmosphere.
Heating Elements: Typically made of materials resistant to high temperatures and hydrogen exposure, such as silicon carbide or molybdenum.
Hydrogen Supply System: Ensures a continuous flow of pure hydrogen into the chamber.
Exhaust System: Safely removes excess hydrogen and byproducts from the chamber.
Temperature Control System: Monitors and regulates the temperature within the furnace.
2. Operation Principle
The material to be processed is placed inside the furnace chamber.
Hydrogen gas is introduced into the chamber, creating a reducing or inert atmosphere.
The heating elements raise the temperature to the desired level, allowing the material to undergo the intended process (e.g., sintering, annealing, or oxide reduction).
After processing, the material is cooled under a controlled hydrogen atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
●Functionalities of Hydrogen Furnaces
1. Oxide Reduction:
Hydrogen acts as a reducing agent, converting metal oxides back to their metallic forms.
2. Protection Against Oxidation:
Prevents the formation of oxides on metals during hightemperature processes.
3. Sintering:
Used for sintering powdered metals or ceramics to achieve highdensity components.
4. Annealing:
Improves the mechanical properties of metals by relieving internal stresses and refining grain structure.
5. Material Synthesis:
Facilitates the synthesis of advanced materials, such as metal hydrides or nanostructured compounds.
●Advantages of Hydrogen Furnaces
1. High Purity Environment:
Hydrogen provides a clean atmosphere, minimizing contamination during processing.
2. Efficient Reduction:
Effectively reduces metal oxides, enabling the production of highpurity materials.
3. Versatility:
Suitable for a wide range of processes, including sintering, annealing, and brazing.
4. Uniform Heating:
Advanced temperature control systems ensure consistent heating across the entire chamber.
5. Scalability:
Available in laboratoryscale and industrialscale models to meet diverse needs.
●Challenges in Using Hydrogen Furnaces
1. Safety Concerns:
Hydrogen is highly flammable and requires strict safety measures to prevent leaks or explosions.
2. Cost:
Highquality hydrogen furnaces and pure hydrogen gas can be expensive.
3. Material Compatibility:
Some materials may react with hydrogen at high temperatures, leading to undesirable effects.
4. Maintenance:
Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure the integrity of seals and heating elements.
5. Complexity:
Requires precise control of hydrogen flow rates and pressure to achieve optimal results.
●Innovations in Hydrogen Furnaces
To address these challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are incorporating advanced technologies:
1. Improved Safety Systems:
Integrated sensors and alarms to detect hydrogen leaks and maintain safe operating conditions.
2. Energy Efficiency:
Advanced insulation and heat recovery systems to reduce energy consumption.
3. Automation:
Programmable controls for precise parameter adjustments and unattended operation.
4. Advanced Materials:
Use of corrosionresistant materials for furnace components exposed to hydrogen.
5. Smart Monitoring:
Realtime data analytics tools for continuous monitoring of processing conditions.
●Applications of Hydrogen Furnaces
Hydrogen furnaces are used across various industries and research fields:
1. Metallurgy:
Sintering of powdered metals to produce highdensity components.
Annealing of steel and other alloys to improve ductility and strength.
2. Ceramics:
Reduction of ceramic oxides for the production of advanced materials.
3. Electronics:
Fabrication of semiconductor materials and thin films under controlled atmospheres.
4. Automotive Industry:
Brazing and heat treatment of automotive parts to enhance durability.
5. Research and Development:
Synthesis of new materials, such as metal hydrides and nanostructures.
●The Future of Hydrogen Furnaces
As technology advances, hydrogen furnaces will continue to evolve to meet the demands of emerging applications. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous systems will optimize processing parameters and reduce human intervention.
2. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and energyefficient designs will become integral parts of future systems.
3. Integration with Advanced Technologies:
IoTenabled furnaces will connect to smart labs for realtime data analysis and process optimization.
4. Development of New Materials:
Advances in hydrogencompatible materials will enable processing of even more challenging substances.
5. Hydrogen Economy:
As hydrogen becomes a key player in the global energy transition, hydrogen furnaces will play a crucial role in material processing and synthesis.
●Conclusion
Hydrogen furnaces are indispensable tools for material processing, offering a unique combination of high purity, efficient reduction, and versatility. Their ability to operate in a controlled hydrogen atmosphere makes them essential for producing advanced materials and improving the properties of metals and ceramics.
What excites you most about the role of hydrogen furnaces in advancing material science and manufacturing? Share your thoughts below! Together, let’s explore how these innovative tools can shape the future of industry and technology.
 English▼
English▼





 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

